IPR MANAGEMENT-Geographical indication
Dr. Tanmoy Mukherjee
Advocate
IPR MANAGEMENT
TANMOY MUKHERJEE
ADVOCATE




Difference between GI & Trademark: -
|
Basis/Subject |
GI |
Trademark |
|
DEFINITION |
A signed used on goods with specific Geographical origin and qualities or reputation due to place. |
A distinctive sign or symbol or identifying goods or services of a particular Source of company. |
|
PURPOSE |
To indicate the origin and quality linked to region. |
To identify and distinguish products of one business from another. |
|
OWNERSHIP |
Owned collectively by producers or associations of region. |
Owned by an individual and company or organization. |
|
NATURE OF RIGHTS |
Collective right used by all registered producers in that region. |
Exclusive right belongs to the trademark owner only. |
|
TRANSFE-RABILTY |
Cannot be transferred or sold. |
Can be assigned, sold or licensed. |
|
SCOPE OF USE |
Only producers in the define region can use the GI. |
Owner has global or national exclusive rights based on registration. |
|
LEGAL PROTECTION |
Geographical Indications of Goods (Registration and Protection Act, 1999). |
Trademark Act, 1999. |
|
EXAMPLE |
Darjeeling Tea, Banarasi Saree, Alphonso Mango. |
Nike, Tata, Amul
. |
|
DURATION |
10 years (Renewable) |
10 years (Renewable). |
|
FOCUS |
Protects place-based identity and traditional knowledge. |
Protects brand identity and commercial Good-Will. |
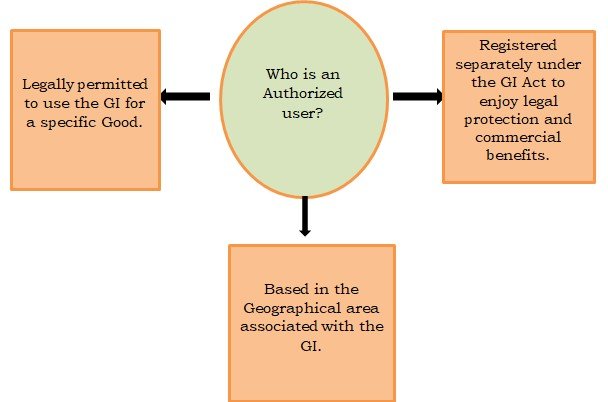
Authorised Users:
Legal Provisions: -
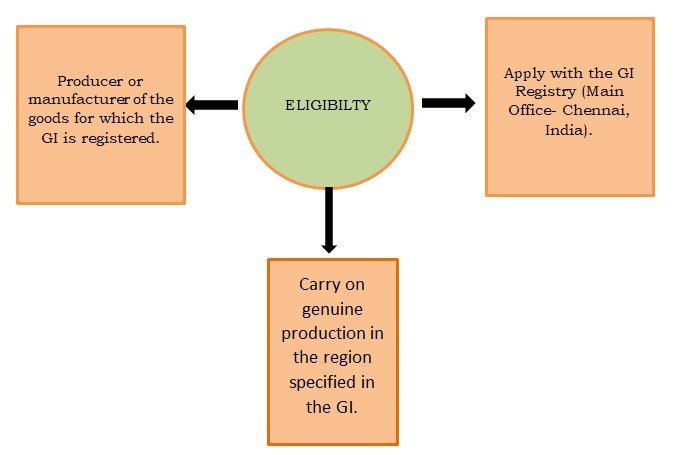
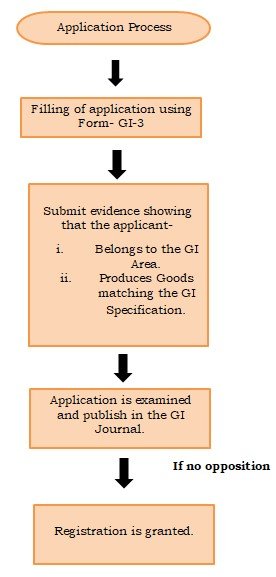
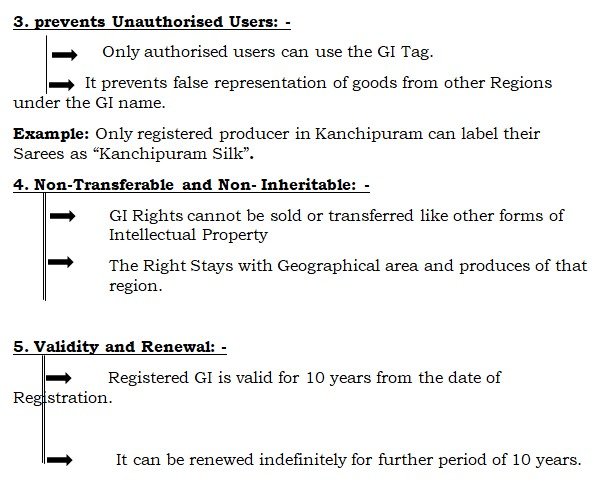
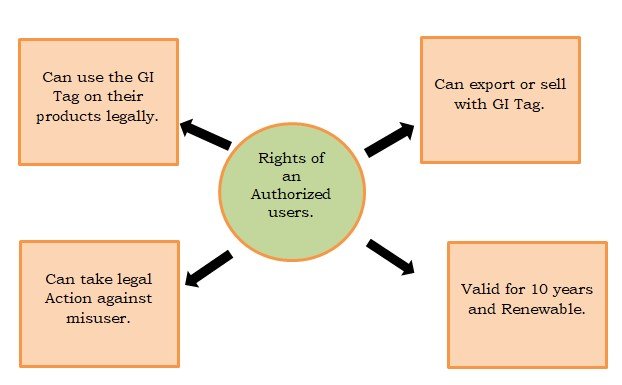
Rights:
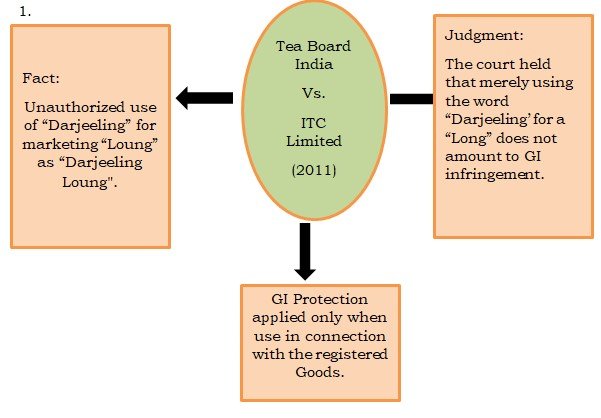
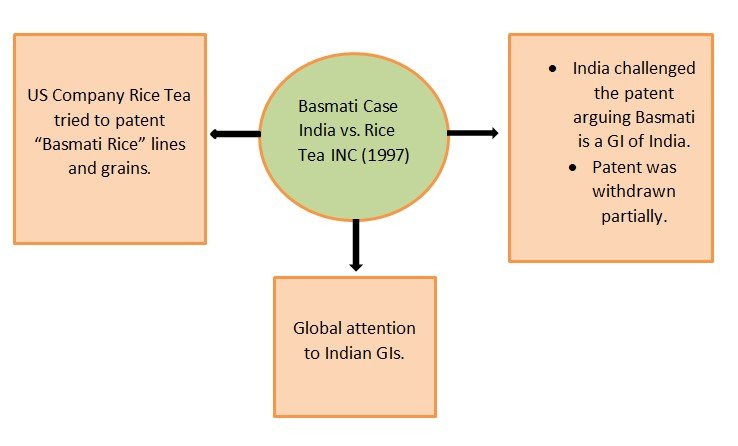
Reference Cases-